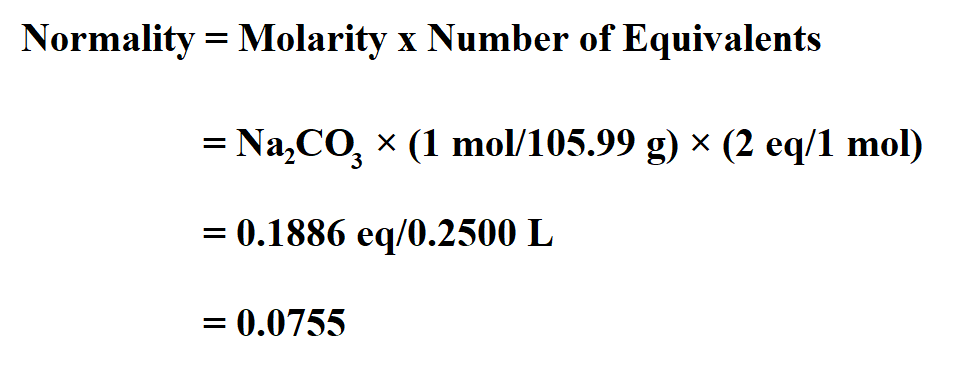Normality is a measure of concentration equal to the gram equivalent weight per liter of solution.
Normality is used in precipitation reactions to measure the number of ions which are likely to precipitate in a specific reaction.
Formula to calculate normality.
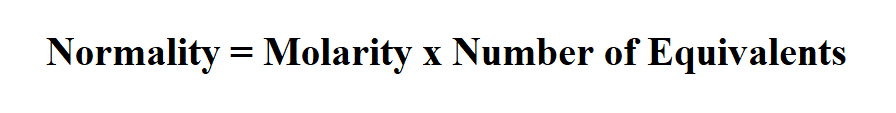
The number of equivalents is a number that defines how many electrons or ions may be transferred in a chemical reaction.
Example:
Calculate the normality of 0.321 g sodium carbonate when it is mixed in a 250 ml solution.
The chemical formula for sodium carbonate is Na2CO3.
Once you have identified that, we see that there are two sodium ions for each carbonate ion. Therefore;